30th Anniversary of UK’s first grid connected solar PV roof

The Oxford Ecohouse was built by Professor Sue Roaf in 1995 to show that a comfortable life could be lived with minimal impact on the climate. It was the focus of international attention with its integrated solar roof combining photovoltaics, solar hot water and passive solar systems. They were designed to provide 100% of the electricity for the low energy house and also charge a Kewet El-Jet electric car. This ordinary, but pioneering home incorporated the first UK grid-connected roof integrated PV system and it caught the imagination of generations. It was used as a teaching tool for architects, engineers, decision makers and the general public alike.
This building has stood the test of time and is working largely as it did in 1995 having integrated now with its local habitats. It still exports around twice as much electricity as it imports and has monthly energy bills that range from £35 to £85 across the year.


Solar Revolutions Party

To celebrate the occasion an event was held on 20th June at the Ecohouse which Steve and Rowan from Wind & Sun were pleased to be invited to.
The reunion brought together many who had actually made the pioneering roof happen then. Those who made the PV cells in Spain (BP Solar) and the hot water system in Findhorn, Scotland (AES Solar), the team were there who designed and built the integrated roof (Bruce Cross GB-Sol) and connected it to the inverter (made by SMA) and grid. Perhaps the most surprising thing was how very early the whole project was, and how visionary all involved were in helping to lay the foundations for the huge solar roof industry today. It was team work back then and it was a joy to celebrate our success together three decades on.
Steve from Wind & Sun had visited during the original installation as he had recently completed the UK’s first grid connected PV system for the Vales’ New Autonomous House in Southwell the year before. Later on, he had helped with maintenance on the system and in replacing the inverter to a newer SMA model in 2006.
See the BBC news article which details the Solar Revolutions Party.


Ecohouse Design Guide

The house was the result of inputs from many different experts and sponsors who contributed to it – working to solve the challenges of the novel systems involved. Many of its lessons were recorded in the popular “Ecohouse Design Guide” that sold tens of thousands of copies in four editions in five different languages.
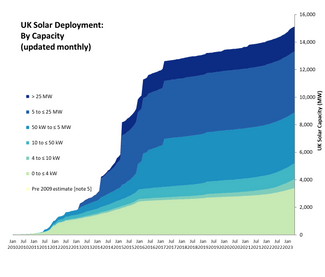
From one house to nearly two million solar buildings today in Britain.
On a quiet road in Oxford back in 1995, history was made.


Below are a few snaps of the day ↓